The document appears to be a technical guide focused on communication buses used in modern computer systems. It provides a detailed overview of serial communication protocols such as RS-232, USB, I²C, and SPI. The guide explains their physical characteristics, data transfer methods, electrical requirements, and advantages/disadvantages. Topics covered include signal encoding, data rates, addressing methods, hardware configurations, and the role of devices like UARTs. It also touches on the historical development and specific implementation nuances for each protocol, highlighting their usage scenarios and design considerations.
- Enseignant: Djillali HAMRI
This document explores the interactions between a microprocessor (or microcontroller) and the outside world via peripherals and input/output (I/O) interfaces. It details the types of peripherals (keyboard, screen, CAN/CNA converters, timers, etc.), their role in data processing and communication, and the controllers used to interface them with the processor. Concepts are illustrated with examples such as the PIC 16F877 microcontroller and various communication buses (USB, Ethernet, etc.).
- Enseignant: Djillali HAMRI
This document provides an overview of microprocessors, detailing their functions, architecture, and components. It defines the microprocessor as a VLSI integrated circuit capable of performing arithmetic and logical operations, managing data transfer, and processing external inputs. The architecture includes a control unit for sequencing instructions, a processing unit containing an ALU for calculations, and internal buses for communication. Additionally, registers store temporary data and addresses to facilitate operations. Lastly, the document describes buses—data, address, and control—which enable communication between the microprocessor and external peripherals.
- Enseignant: Djillali HAMRI
Intelligent Control Systems studies the method of control systems design using fuzzy control and
neural network, and optimization using genetic algorithm. Design of basic rules of fuzzy systems
of the Mamdani and Sugeno types use heuristic method are discussed. The Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy
model is used to represent the dynamics of a nonlinear system on the basis of rules for
controllers using the concept of Parallel Distributed Compensation. Validation of fuzzy system
design is applied to real systems. Neural network methods are also discussed and used for system
control purposes, while genetic algorithms are usedto solve optimization problems in the control
system.
- Enseignant: Bouziane Meliani
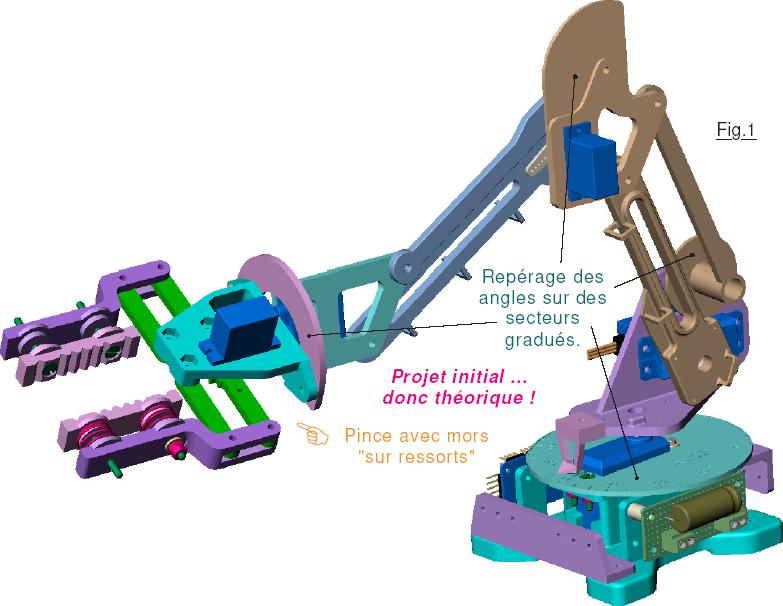
The objective of this course is to enable students to master the modelling tools and control techniques for manipulator robots. It aims to give students the opportunity to undertake independently the resolution of a certain number of elementary robotics problems such as configuration, trajectory generation, dynamic control, etc.
- Enseignant: Karim Belalia

This course is aimed at Master 2 students in electrical engineering, industrial electrical engineering options, who are about to prepare their final project. Indeed, all Master 2 students are concerned and need to acquire a good methodology to prepare their final projects.
The content of this course is in line with the official program issued by the French Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research. Through the various chapters, the reader will be introduced to documentary research and learn about the stages, methodology and ways of writing and presenting a dissertation.
In short, this course is a tool designed to help students prepare their dissertation from start to finish, and to give them the right approach to follow.
- Enseignant: abdelkader mostefa

Industrial computing is crucial because it enables automation, precision, and efficiency in modern industries. By integrating computers into industrial processes, companies can optimize production, reduce human error, and enhance quality control.
- Enseignant: Djillali HAMRI
- Enseignant: benyssaad yssaad

- Enseignant: benyssaad yssaad
- Enseignant: Hakim Ait Said