.L’Algérie a adopté en février 2011, un programme ambitieux des énergies renouvelables et de l’efficacité énergétique . Toute l'attention des pouvoirs publics est mobilisée afin de réussir ce programme basé sur une stratégie verte tracée à l’horizon 203. Le programme de l’efficacité énergétique affiche la volonté de l’Algérie de préserver les ressources du pays et optimiser leurs utilisation

- Teacher: Malika Safer
L’objectif de ces travaux pratiques est d’acquérir les connaissances de Physique de la matière condensée et de développer des méthodes et des connaissances sur l'obtention et le traitement des données expérimentales.
- Teacher: Youcef Cherchab
- Teacher: Sarah Oufella
The objective of this course is to present the fundamental principles governing laser operation. It is based on the rate equations describing the population dynamics of energy levels in a laser medium and on the characterization of the general properties of laser radiation.
- Teacher: Amel Slamani
Understand the significance of semiconductors in the design and implementation of electronic components. Master the transport mechanisms and physical phenomena governing the operation of discrete electronic components
.
- Teacher: Amel Slamani
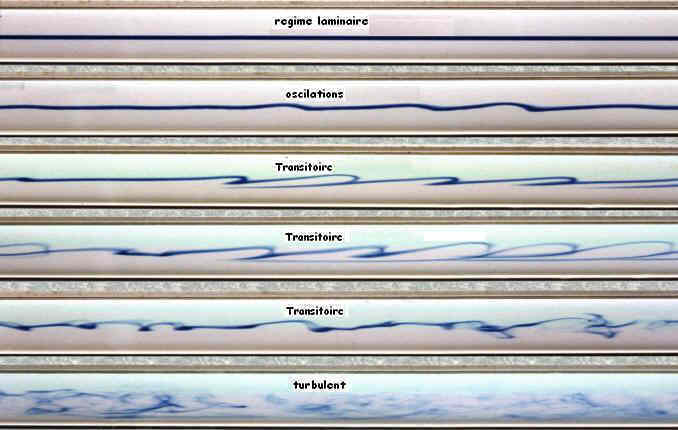

Les équations de Reynolds sont des équations fondamentales en mécanique des fluides, particulièrement utilisées pour décrire l'écoulement turbulent. Elles sont dérivées des équations de Navier-Stokes en effectuant une décomposition des variables d'écoulement en une composante moyenne et une composante fluctuante. Ce cours détaillé abordera les aspects suivants :
1. Introduction et contexte
2. Décomposition de Reynolds
3. Dérivation des équations de Reynolds
4. Termes de contrainte de Reynolds
5. Fermeture des équations de Reynolds
6. Applications et limitations
- Teacher: fares redouane
The optical properties of solids provide an important tool for studying energy band structure, impurity levels, excitons, localized defects, lattice vibrations, and certain magnetic excitations. In such experiments, we measure some observable, such as reflectivity, transmission, absorption, ellipsometry or light scattering; from these measurements we deduce
the dielectric function esp(w), the optical conductivity σ(w), or the fundamental excitation
frequencies. It is the frequency-dependent complex dielectric function esp(w) or the complex
conductivity σ(w), which is directly related to the energy band structure of solids.
- Teacher: Bachir Bouhadef